Sending Build Info
Overview
If projects require artifacts that are not publicly accessible, or have unique environmental requirements that preclude agents from gathering build information, the send_build_info.sh script can be used to send build information to the CodeLogic server.
It is run in the Git working tree and sends the following information gathered from Git:
- Git author
- Git author email
- Git branch
- Git commit hash
- Git commit message
- Git repository URL
The script also sends this information, specified by the user:
- Build log
- Build number
- Build status
- Job name
- Node name
- Pipeline system
Important: The script only works with pre-authorized agents. That is, agents that are created from the CodeLogic UI.
Create an Agent in the CodeLogic UI
Navigate to the Agents page from the side navigation bar in the CodeLogic UI
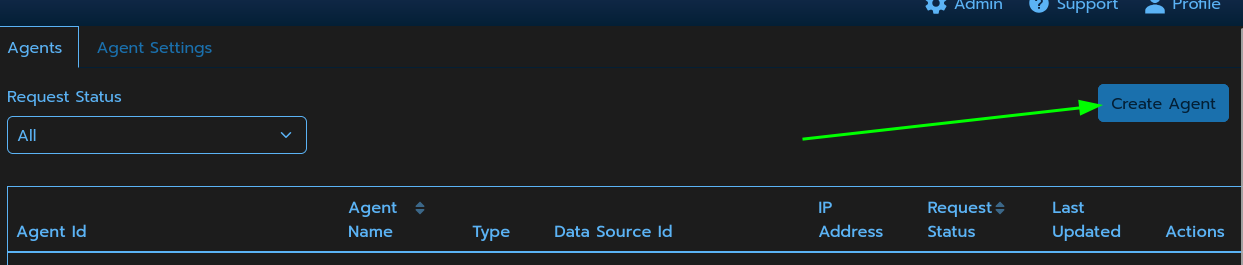
Create a new agent by clicking Create Agent on the Agents page and giving the agent a name and optional description.
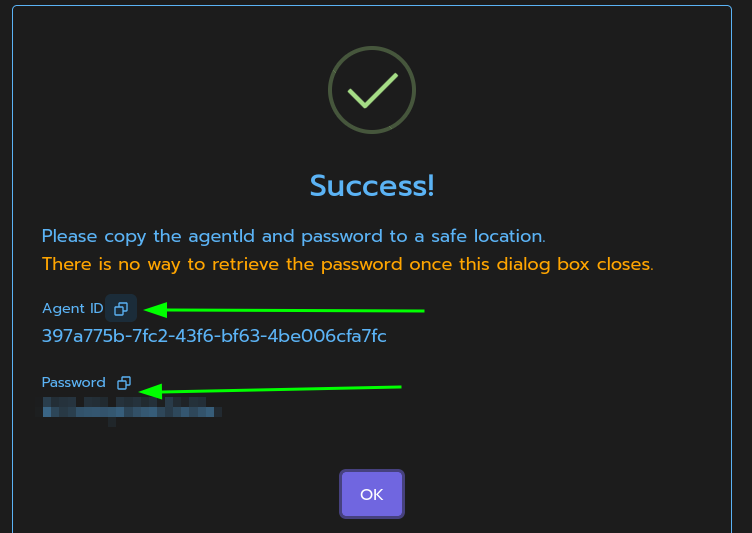
Note the Agent ID and Password, or leave this modal open.
Installation
There are multiple ways to install the send_build_info.sh script:
Through the UI
Download the script under Store > Miscellaneous
Directly from the CodeLogic server
For Linux systems and Windows with WSL2, you can use the following command:
wget ${SERVER_LOCATION}/codelogic/server/packages/send_build_info.tar -O /tmp/send_build_info.tar && tar -xvf /tmp/send_build_info.tar -C /tmp
Using the Store Interface
The CodeLogic UI provides a convenient Store interface to generate Docker commands for sending build information. This is the recommended method for most users as it eliminates the need to manually construct complex Docker commands.
Accessing the Store
- Navigate to the
Storepage from the side navigation bar in the CodeLogic UI - Scroll down to the
Dockersection - Click on the
Send Build Informationtile
Using the Send Build Information Generator
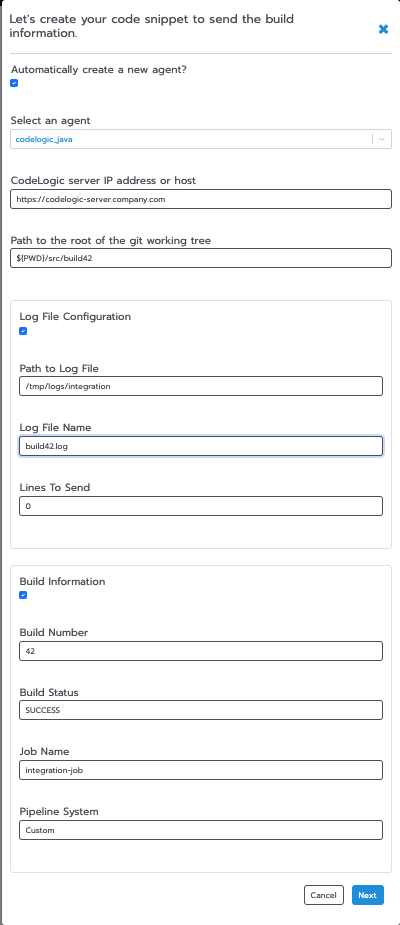
The Store interface provides a step-by-step form to configure your build information:
- Agent Configuration: Select an existing agent or create a new one
- Server Configuration: Specify your CodeLogic server address
- Log File Configuration (optional): Configure log file settings
- Build Information (optional): Specify build details like build number, status, job name, and pipeline system
The generator will create a Docker command that you can copy and run in your terminal. The generated command includes all necessary volume mounts and environment variables.

Operation
$ ./send_build_info.sh --help
Note: When using volume mounts with -f or --log-file, the system intelligently combines paths:
Case 1: -v /opt/codelogic/sql/logs:/log_file_path -f myLogFile.txt
→ Creates /log_file_path/myLogFile.txt
Case 2: -v /opt:/log_file_path -f codelogic/sql/logs/myLogFile.txt
→ Creates /log_file_path/codelogic/sql/logs/myLogFile.txt
Case 3: -v /opt/codelogic/sql:/log_file_path -f logs/myLogFile.txt
→ Creates /log_file_path/logs/myLogFile.txt
Usage: send_build_info.sh [OPTIONS]...
Send build information to the CodeLogic server.
This script is intended for environments in which build information is not
accessible. Use it to send Git, build, and related information to the CodeLogic server.
The Agent UUID and password are supplied by the CodeLogic server when an agent
is created manually in Agents > Create Agent.
It must be run from within your Git working tree directory, or use -P/--path to specify
the absolute path to the Git repository directory.
Temporary files are created with unique names (including process ID) in /tmp and are
preserved by default. Use --cleanup-temp-files to automatically delete them.
Required Options:
-a, --agent-uuid=AGENT_UUID Agent UUID for CodeLogic server authentication
(can also be set via AGENT_UUID environment variable)
-P, --agent-password=PASSWORD password for the agent (can be set via AGENT_PASSWORD
environment variable, will prompt if not specified, to avoid
storing in command line history, timeout after 300 seconds)
-s, --server=SERVER_URL the full URL of the CodeLogic server (supports both HTTP and HTTPS)
(can also be set via CODELOGIC_HOST environment variable, or found in
installation files: /opt/codelogic/codelogic.config,
/opt/codelogic/java/application.yml, /opt/codelogic/sql/application.yml)
(e.g., http://192.168.86.50 or https://codelogic-server.example.com)
CLI options take precedence over environment variables, which take precedence over configuration files
Optional Options:
-b, --build-number=NUMBER specify the build number (default: 1)
-c, --cleanup-temp-files delete temporary files after successful completion or on exit
(default: false - temporary files are preserved with unique names)
-d, --dry-run print planned work without executing
--test synonym for --dry-run (test configuration without executing)
-f, --log-file=FILE specify a log file to use instead of creating one. The entire log file
will be sent by default (use -n/--log-lines to customize). If not specified,
a file will be created with job-name, build-number, build-status, pipeline-system,
hostname, and user.
-i, --pipeline-system=SYSTEM specify the pipeline system (default: Custom),
other options: Custom, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, etc.
-j, --job-name=JOB_NAME specify the job name (default: unknown-job)
-n, --log-lines=NUMBER specify the number of trailing lines to send from the log file
(default: entire file, min: 5, max: 50000).
This option is only used when a log file is specified using --log-file.
If not specified, the entire file is sent. Common values: 1000, 5000, 10000, 50000 lines.
-p, --path=PATH specify the absolute path to the Git repository directory to analyze
(default: current working directory). Must be an absolute path starting with /.
-t, --build-status=STATUS specify the build status (default: SUCCESS)
-T, --timeout=SECONDS specify timeout for network operations in seconds (default: 30, min: 5, max: 300)
-v, --verbose run with extra logging
-h, --help display this help and exit
Examples:
# DOCKER USAGE (Primary method):
# Mount your code directory and run via Docker:
docker run -v /path/to/your/code:/scan -v /path/to/logs:/log_file_path your-image send_build_info \
--agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" --server="https://codelogic-server.example.com"
# Mount both code and log directories:
docker run -v /path/to/your/code:/scan -v /path/to/logs:/log_file_path your-image send_build_info \
--agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" --log-file="/log_file_path/build.log"
# Basic Docker usage with build log:
docker run -v /home/user/myproject:/scan -v /home/user/logs:/log_file_path your-image send_build_info \
--agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" --server="http://192.168.86.50" \
--log-file="/log_file_path/build.log"
# Docker with environment variables:
docker run -v /home/user/myproject:/scan \
-e AGENT_UUID="agentuuid" -e AGENT_PASSWORD="agentpassword" -e CODELOGIC_HOST="http://192.168.86.50" \
your-image send_build_info --log-file="/scan/build.log"
# Access temporary files from host system:
docker run -v /path/to/code:/scan -v /path/to/local/directory:/tmp your-image \
send_build_info --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword"
# STANDALONE USAGE (Advanced users):
# The following examples assume you're running the script directly on a system with the code:
# Basic usage, from a Git working tree directory
./send_build_info.sh -a "agentuuid" -P "agentpassword" -s "https://codelogic-server.example.com" -f "/path/to/build.log"
# Using long flag for server, from a Git working tree directory, default build log file
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--server="https://codelogic-server.example.com"
# Long option with equals sign
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--server="http://192.168.86.50" --job-name="my-job" --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Verbose mode
./send_build_info.sh -v -a "agentuuid" -P "agentpassword" \
-s "https://codelogic-server.example.com" -j "build-job" -b 456 -t "SUCCESS" -i "Jenkins"
# Using environment variables
export AGENT_UUID="agentuuid"
export AGENT_PASSWORD="agentpassword"
export CODELOGIC_HOST="https://codelogic-server.example.com"
./send_build_info.sh --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Using custom log file with specific number of lines
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--log-lines=500 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Common log line presets for large build logs
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--log-lines=1000 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--log-lines=5000 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--log-lines=10000 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--log-lines=50000 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Using timeout for slow networks
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--timeout=60 --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Clean up temporary files after completion
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" \
--cleanup-temp-files --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Server URL optional if found in configuration files
./send_build_info.sh --agent-uuid="agentuuid" --agent-password="agentpassword" --log-file="/path/to/build.log"
# Specify custom Git repository path
./send_build_info.sh -a "agentuuid" -P "agentpassword" -s "https://codelogic-server.example.com" -p "/path/to/git/repo"